The first example problem is pretty basic. D a b.
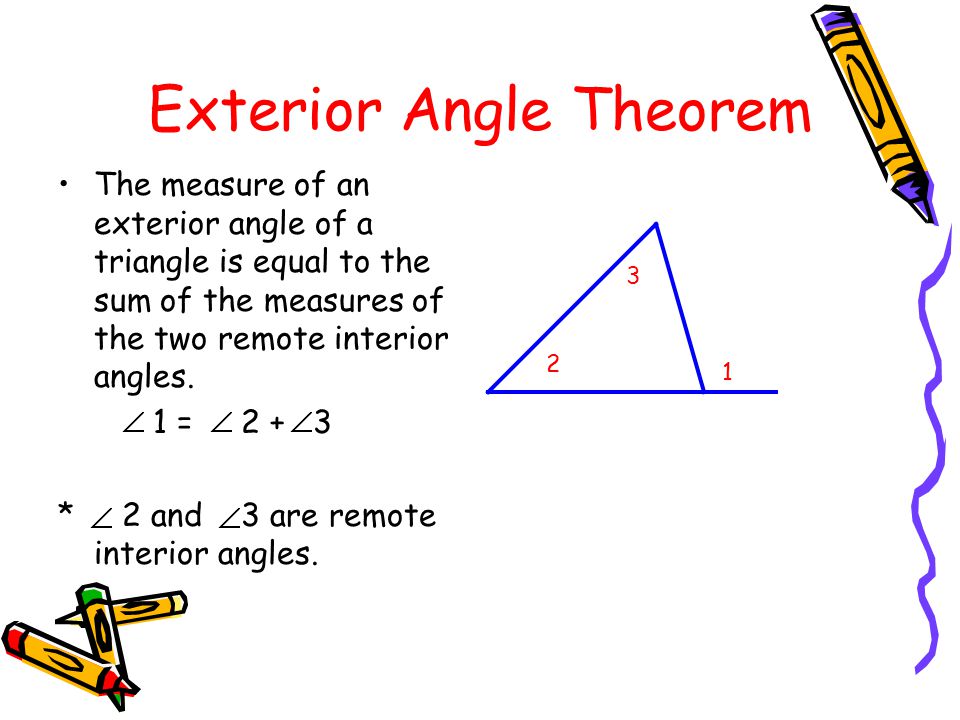
Although only one exterior angle is illustrated above this theorem is true for any of the three exterior angles.
F.3 exterior angle theorem. This is a fundamental result in absolute geometry because its proof does not depend upon the parallel postulate. This theorem is a shortcut you can use to find an exterior angle. The exterior angle inequality theorem states that the measure of any exterior angle of a triangle.
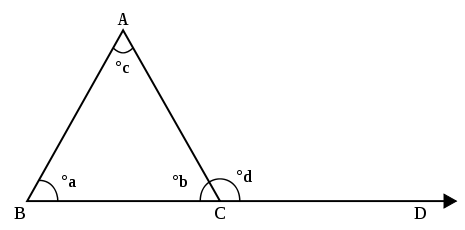
So d c equals a b c. The exterior angle theorem states that the measure of each exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite and non-adjacent interior angles. This theorem is Proposition 116 in Euclids Elements which states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of the measures of the remote interior angles.
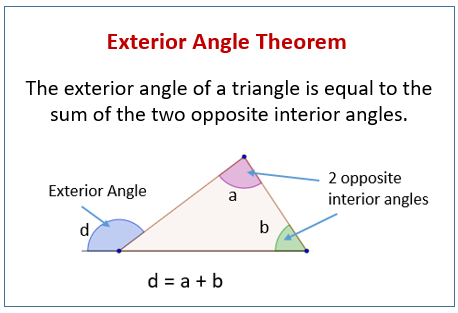
Two example problems are solved in detail. The Exterior Angle Theorem states that An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles. Using the formula we find the exterior angle to be 3606 60 degrees.
The missing angle is 86º. Terms in this set 50 The missing angle is 122º. Subtract c from both sides.
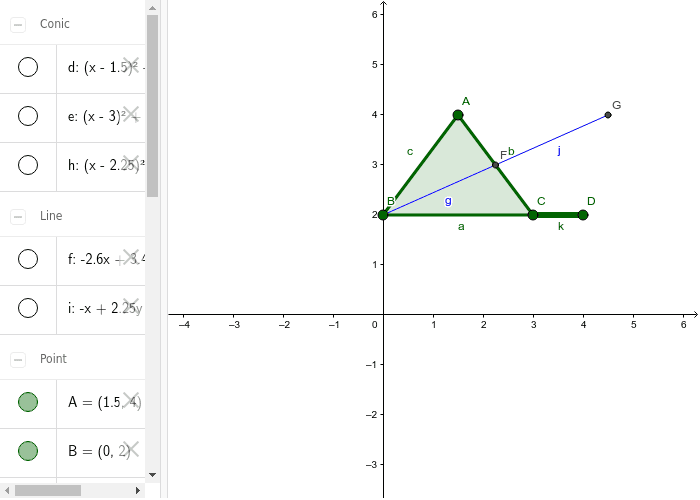
This theorem is also known as the high school exterior angle theorem or Euclids exterior angle theorem. Exterior Angle Theorem The exterior angle theorem states that if a triangles side gets an extension then the resultant exterior angle would be equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles of the triangle. Exterior and Interior Angle Theorem Construct the geometric object by following the instructions below and then answer the questions about the object.
Click Create Assignment to. The missing angle is 85º. D b a.
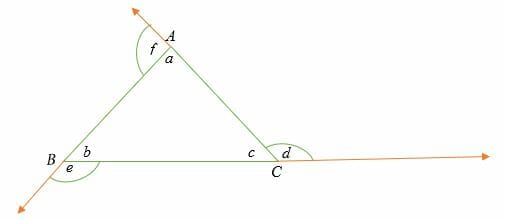
Remember that the two non-adjacent interior angles opposite the exterior angle are sometimes referred to as remote interior angles. Angles c and d make a straight angle which is 180. For example in triangle ABC above.
The missing angle is 77º. Create a triangle and label it ABC. In the figure above drag the orange dots on any vertexto reshape the triangle.
This is very easy to prove. From the Measure Toolbar select Angle. A b c 180.
M 4 m 1 m 2. D c a b c. Triangle Exterior Angle Theorem This video discusses the exterior angle theorem.
For this example we will look at a hexagon that has six sides. The missing angle is 75º. Exterior Angle Theorem An exterior angle of a triangle is formed by any side of a triangle and the extension of its adjacent side.
Because the interior angles of a triangle add to 180 and angles cd also add to 180. Exterior Angle Theorem The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two non-adjacent interior angles of the triangle. The second example problem is much harder.
D c 180. Count the number of sides of the polygon being analyzed. The missing angle is 26º.
The exterior angle theorem states that the measure of an exterior angle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two remote interior angles of the triangle. EXTERIOR ANGLE THEOREM This theorem is Proposition 116 in Euclids Elements which states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of the measures of the remote interior angles. This is a fundamental result in absolute geometry because its proof does not depend upon the parallel postulate.
This states that any exterior angle BCD of a triangle equals the sum of both interior angles A and B at the other 2 triangle vertices. The exterior angle theorem states that the exterior angle formed when you extend the side of a triangle is equal to the sum of its non-adjacent angles. Next calculate the exterior angle.
The Exterior Angle Theorem says that if you add the measures of the two remote interior angles you get the measure of the exterior angle. 2 Exterior Angle Theorem. Measure the three interior angles of the triangle and label the measurements.
It also define what exterior and remote interior angles are. In the above diagram. The sum of all 3 angles in a triangle always equals 180.
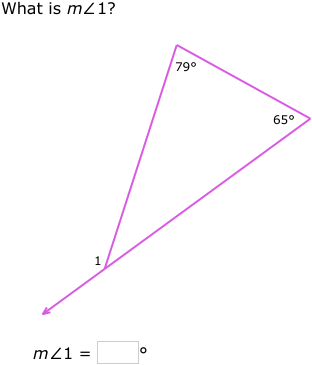
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles. The missing angle is 79º. The interior angles of a triangle add to 180.
This concept teaches students the sum of exterior angles for any polygon and the relationship between exterior angles and remote interior angles in a triangle.
Ixl Exterior Angle Theorem Geometry Practice

Exterior Angle Triangle World Mathematics Remote Theorem Worksheet Sumnermuseumdc Org
Interior Angles Of A Triangle Wild Country Fine Arts
Exterior Angle Theorem Wikipedia
Exterior Angles Theorems Read Geometry Ck 12 Foundation

Exterior Angle Theorem Definitions Facts And Solved Examples Cuemath
Exterior Angles Theorems Read Geometry Ck 12 Foundation

Ixl Exterior Angle Theorem Geometry Practice
Interior Angles Examples Wild Country Fine Arts
Exterior Angle Theorem Proof Geogebra

Ixl F 3 Exterior Angle Theorem Youtube
Mrwadeturner M4 Exterior Angles And Sss

Exterior Angle Theorem Explanation Examples

Exterior Angle Theorem Definitions Facts And Solved Examples Cuemath

Ixl F3 Exterior Angle Theorem Geometry Youtube

Exterior Angle Triangle World Mathematics Sums Worksheet Sumnermuseumdc Org
Notes Lesson 3 2 Exterior Angle Theorem Interior Interior Exterior Example 1




0 Comments